INTRODUCTION
This
chapter provides descriptions on the background of study, problem statement,
objectives of the study and scope of the study.
BACKGROUND OF STUDY
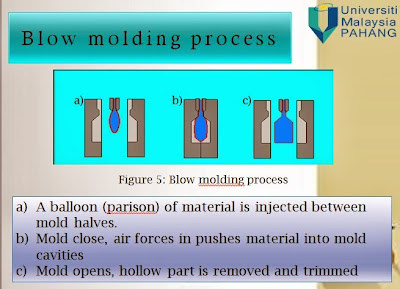
Blow moulding is a manufacturing process that used to create hollow plastic parts by inflating a heated tube until it fills a mould and forms that desired shape. It is a moulding process in which air pressure is used to inflate soft plastic into a mould cavity. It is an important industrial process for making one piece hollow plastic parts with thin walls, such as bottles and similar containers. Since many of these items are used for consumer beverages for mass markets, production is typically organized for very high quantities. The technology is borrowed from the glass industry with which plastics compete in the disposable or recyclable bottle market. (Pepliński.K and Mozer.A 2010). Blow moulding is accomplished in three steps which are design and simulation by using software, fabrication of a starting tube of molten plastic called a parison (same as in glass-blowing) and inflation of the tube to the desired final shape. Forming the parison is accomplished by either of two processes which are extrusion or injection moulding. Blow moulded parts can be formed a variety of thermoplastic material, including Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE), High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Polypropylene (PP), and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC). The advantages are it is very cheaper process than injection moulding multiple product methods which it used for producing receptacles in large quantities where the melted polymer is injected into the mould than blow through using air and the disadvantages it limited to hollow forms and the wall thickness is also hard to control as the larger the product being gets, the thinner polymer has to be stretched. The basic application on blow moulding process has two fundamental phases which are a parison of hot plastic resin in a somewhat tubular shape is created and it compressed air is used to expand the hot preform and press it against mould cavities. (Guide for extrusion blow molding; Advanced elastomer system). This project is delegate to investigation on simulation on polypropylene using the different diameter of parison and wall thickness distribution using ANSYS software. ANSYS software has the ability to detect contact between a free surface and a wall that occurs over time. The wall is typically a mould for blow moulding and thermoforming simulations, although the contact detection feature can be applied to other processes. The contact detection algorithm is applicable only for time dependent problems. After a free surface and wall have come into contact, it is possible to simulate their detachment under specific circumstances. Contact release typically takes place when the motion of a mould is reversed, or when the forming pressure results in the material being pulled away from a mould. (Ansys Inc., 2010). A significant factor in the design stage of new blowing product is selection parison shape in order to obtain the best distribution of final wall thickness in the bottle. Four different diameter of parison were considered. This software can perform a number of complex calculations which are multi domain simulations, co-extrusion of several fluids and three-dimensional extrusion. A time dependent problem is defined and setting material properties and boundaries condition for a 2D axisymmetric bottle blow molding. Numerical data available in Polydata(setup) for a time dependent problem Ansys sofware were applied. (Gupta.S and Uday.V 2013). This project will use the plastic material which is polypropylene. Polypropylene is a common plastic used for blow moulding. It offers many advantages over other blow moulding resins. A high heat distortion temperature allows its use in hot fill applications. The ability to be autoclaved without excessive haze or colour development enables it to be used in medical applications. It also has excellent environmental stress cracking resistance, as well as chemical and solvent resistance. Polypropylene has good contact clarity, low colour, and very low moisture transmission rates, all of which make it ideal for blow moulding applications. (Richardson and Lokensgard 1997)
PROBLEM STATEMENT
For a past year, there is a lot of techniques blow molding to produce the hollow part by using the plastic as the material. On conventional machine, blow molding of heavily convoluted, three-dimensional tubular shapes, such as fuel tank filler pipes, automotive air ducts, tubes used in household appliances, inevitably results in welding seams at the pinch areas causing potentially large amounts of flash at the mold parting line. It also only uses trial and error method to produce mold and parison where it is more investment in capital company to produce the part. In this project, the project statement and knowledge is very limited such as finding journal, previous research and this software is very limited to find the tutorial as reference. To overcome the problem, blow molding technologies offer minimum flash production achieving significant savings in material, energy usage, cycle times and, capital spending. It also can choose the best parison to use in blowing process. In 2D blow molding, a parison sized according to the diameter is manipulated by Ansys software directly into the cavity of the blow mold to avoid defect areas on the surface of bottle and minimizing overall material usage and also the thickness on the bottle. Using Ansys software it can make the fast result, reduce the time step, and it is 90% accurate with the actual process. It also can determine the stress occurs on the bottle part. Basically to produce this part only using polypropylene (PP) as the material because it can improve the mechanical properties to be good, heat resistance good to chemical, good flow, and processibility. Therefore, this project wants to analyze the effect on the final wall thickness with different diameter of parison and stress contour occurs. This project are been done to gather more information to predict the result as in the actual blowing process.
OBJECTIVES
The main objectives of
this project are:
1) To
design and simulate the different parison diameter via ANSYS software.
2) To
analyze the effect on the final wall thickness with different diameter of
parison and stress contour occurs.
3) To
validate the results of simulation works.
SCOPE OF PROJECT
This project is focus on the materials, simulation process work, parison diameter and thickness on the bottle where 8, 10, 18, and 20mm diameter of parison will use to investigate the effect on final wall thickness and contour stress by using ANSYS software. The graphical of bottle is followed by Pepliński.K and Mozer.A (2010) journal but the design of the mold and parison shape used with the different diameter. In this software the method to produce the part is using blow molding technique which is extrusion blow molding. This techniques begin the large pressure which is 2.0Mpa is applied to perform which enters the mold and the parison will expand eventually takes its shape. Times steps during the parison expand to contact the cavity wall is 0.1s. The ANSYS software has been used as 2D blow molding simulation tools in order to simulate the behavior of characteristics of part produce with different diameter parison. After the simulation process completed, the wall thickness will be investigate by see the effect on the final wall thickness and stress contour occurs through the software. As the conclusion the best results of the selection parison using polypropylene material are suggested for improvement some recommended in the future work.
1.4
1.5



Welcome...
ReplyDeleteWelcome...
ReplyDelete